Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), How It Works, Advantages and Disadvantages

What is ERP system
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a unified modular software system which integrates various functional areas of an organization’s business processes.
How does ERP work?
An ERP system includes various components which are called modules, that focus on different business areas like finance, accounting, HR, production, customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management, etc.
Depending upon the requirements of the business, some or all core modules are used.
An ERP system has a central database from which the various modules access and share information involved in the business process, that’s how erp works in an organization.
As the system shares the data, there is monetary benefits, accuracy, and collaboration between the departments of the organization.
It negates the need for siloed software systems and unifies various systems which enable growth of the organization.
Types of ERP implementation
ERP implementation includes on-premises, cloud and a mix of the two called a hybrid version.
The cloud version enables easier deployments in a short period of time by using Software as a service (SAAS) or Platform as a service (PAAS) systems.
Legacy ERP systems were large, complex, homogeneous systems that are not always compatible with a cloud service delivery model.
These ERP systems developed by software vendors are run on premises.
The deployment of a new ERP system in-house requires business process re-engineering (BPR), employee training sessions and back-end support for database integration, data analytics and reporting.
Presently, a large number of companies are moving to cloud-based ERP, especially SaaS and hybrid ERP models.
This ERP software runs on premises as well as in the cloud.
Cloud-based ERP modules are built in such a way that the deployment requires less the cost and time.
Cloud-based ERP does not require the hardware and infrastructure for on-premises implementations which saves costs.
They can be easily upgraded and scaled up with time.
Some ERP systems offer support for artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced analytics.
Many organizations run multiple ERP systems under one environment which is known as two-tier or multi-tier ERP systems.
The need for such systems arises due to geographic differences in the organization, divisions running different systems or even company mergers.
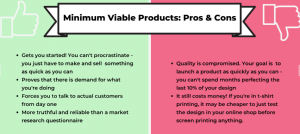
Benefits of ERP systems
ERP offers many benefits due to information sharing and standardization.
The ERP components can share data so cross-departmental business processes become easier to manage.
It enables better insights from business data as they are compatible with analytics, machine learning, and industrial IoT tools.
These systems help in automating data collection and enable business growth by managing complex business processes.
It helps in lowering risk by enabling better compliance.
ERP systems help in providing better business insights and intelligence, customer services and improve supply chain management.
They also help with better reporting, planning and data security, along with improved data backup and access control.
Disadvantages of ERP systems
In house ERP systems implementation and configuration usually, have a high upfront cost and complexity.
It requires change management during and after implementation.
An organization may need to hire additional IT staff, consultants, training specialists, for development and maintenance.
Vendors offering ERP systems charge a fee for maintenance on top of the license fee as well.
Investment in new hardware might also be required to support the new ERP system, such as servers.
Customization of ERP software takes a lot of time, effort, expertise and money and sometimes the budget overruns along with deadlines.
The ERP modules may be less useful and sophisticated compared to stand-alone software systems.
Companies may require additional modules for better management of specific functional areas such as the supply chain or customer relationship management.